Do You Grind Your Teeth in Your Sleep? What It Means and How to Stop
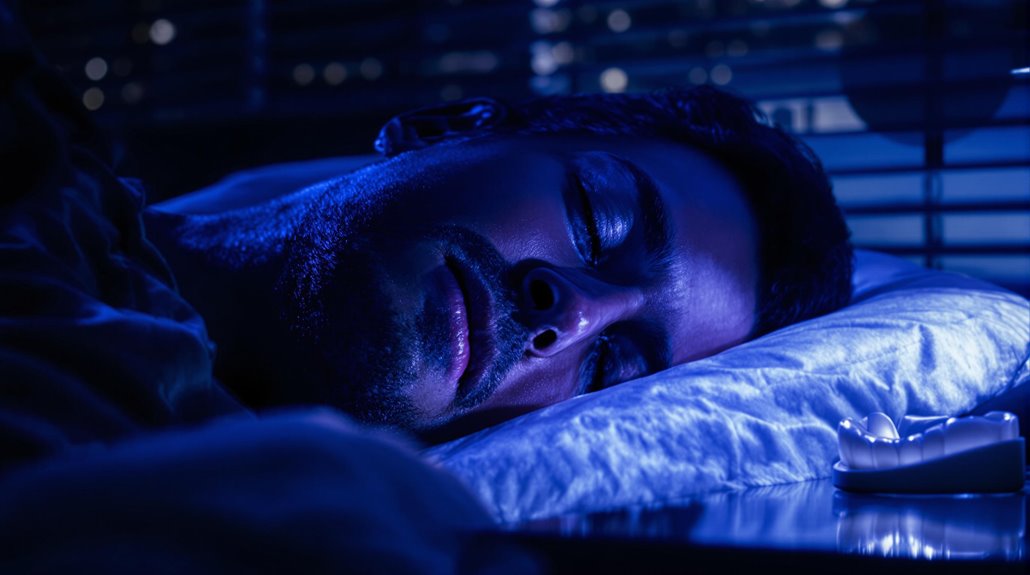

If you wake up with headaches, jaw pain, or your partner hears grinding noises at night, you might be one of the many adults who grind their teeth while sleeping. This common condition, called sleep bruxism, can damage your teeth and cause chronic pain if left untreated. Stress, anxiety, sleep disorders, and certain medications often trigger teeth grinding. You can protect your teeth with a custom mouth guard, practice stress management techniques, and improve your sleep habits. A combination of dental care and lifestyle changes can help you break this harmful habit, and there's more you can do to protect your smile.
Understanding Sleep Bruxism
Nearly half of all adults unknowingly grind their teeth while sleeping, a condition known as sleep bruxism. If you're experiencing unexplained jaw pain, headaches, or dental problems, you might be one of them. Sleep bruxism involves more than just teeth grinding - it can also include jaw clenching and gnashing that occurs while you're asleep.
What's particularly challenging about sleep bruxism is that its causes aren't fully understood. You might develop this condition due to a combination of physical, psychological, and genetic factors. It's often linked to other sleep disorders, particularly sleep apnea and snoring, which can complicate both diagnosis and treatment.
Left untreated, teeth grinding can lead to serious complications. You're at risk for significant tooth damage, wear on your temporomandibular joint (TMJ), and chronic jaw pain. The good news is that various treatment options are available. Your dentist can diagnose sleep bruxism through a dental examination, and they might recommend a sleep study to confirm the diagnosis. Treatment approaches range from custom-made mouth guards and behavioral therapy to medication, depending on the underlying causes of bruxism and severity of your symptoms.
Signs You Grind Your Teeth
Recognizing the signs of teeth grinding is the first step toward addressing sleep bruxism. If you wake up with frequent headaches, especially in the morning, this could indicate you're clenching teeth while sleeping. Pay attention to any jaw pain or tenderness you experience during the day, particularly when you're eating, as chewing problems often signal ongoing teeth grinding.
Physical changes to your teeth can provide clear evidence of sleep bruxism. Look for worn teeth that appear flattened or have developed chips along their edges. If you notice clicking jaw sounds or a popping sensation when opening and closing your mouth, you might be developing TMJ issues as a result of nighttime grinding.
Your sleeping partner can be an informative source of information. If they've mentioned hearing grinding sounds while you sleep, take this as a definitive sign of sleep bruxism. The combination of these symptoms - morning headaches, jaw pain, dental wear, TMJ problems, and grinding noises - strongly suggests you're grinding your teeth at night. Identifying these signs early can help prevent more serious complications from developing.
Common Triggers and Risk Factors
Life's daily pressures often lie at the root of teeth grinding, with stress and anxiety serving as the primary triggers for this unconscious habit. If you're experiencing bruxism, understanding what causes your jaw clenching can help you address the underlying issues.
Beyond stress, several key factors can increase your likelihood of grinding your teeth during sleep:
- Sleep disorders, particularly sleep apnea, can trigger episodes of teeth grinding as your body attempts to maintain open airways during the night
- Certain medications, especially some antidepressants, may intensify bruxism as a side effect of their chemical interactions with your brain
- Your lifestyle choices, including smoking, alcohol consumption, and caffeine intake, can profoundly worsen teeth grinding patterns
- Your genetic makeup and personality type play a role, as researchers have found that people with aggressive or hyperactive personalities are more prone to bruxism
Understanding these triggers is vital because they often work in combination. For instance, if you're genetically predisposed to bruxism, high caffeine consumption and stress might compound the issue, making your teeth grinding more severe during sleep.
Health Impacts of Teeth Grinding
Through constant grinding and clenching, bruxism can wreak havoc on your oral and overall health. When you're grinding your teeth regularly, you'll likely experience a range of uncomfortable symptoms that can greatly impact your daily life, including persistent headaches, facial pain, and difficulties with jaw movement.
Sleep bruxism doesn't just affect your teeth - it can lead to serious complications if left untreated. Clenching your teeth puts excessive pressure on your temporomandibular joint (TMJ), potentially causing TMJ disorders that make it painful to eat, speak, or even open your mouth fully. You might also notice earaches, tinnitus, and soreness in your jaw muscles. The dental damage from teeth grinding can be severe, resulting in worn-down enamel, sensitive teeth, and even tooth loss in extreme cases.
Beyond the immediate discomfort, chronic pain from teeth grinding can disrupt your sleep patterns and contribute to sleep disorders. This creates a troubling cycle, as poor sleep quality often worsens bruxism symptoms. The condition may also be linked to other health issues, including sleep apnea and mental health concerns, making proper diagnosis and treatment essential for your overall well-being.
Diagnosis and Professional Assessment
Getting a proper diagnosis for teeth grinding starts with a visit to your dentist, who'll conduct a thorough examination of your mouth and jaw. During the dental exam, your dentist will look for signs that you grind your teeth, examining potential teeth changes and damage that may have occurred over time. They'll also ask questions about your patient history, including your sleep habits, medications, and daily routines, to better understand potential triggers for your teeth grinding.
To determine if you have bruxism, your dentist will evaluate whether it's a progressive condition that requires immediate treatment. In some cases, they may recommend a sleep study (polysomnography) to confirm sleep bruxism and rule out other sleep disorders.
During the diagnostic process, your dentist will assess:
- Physical evidence of wear patterns on your teeth and any changes noticed between visits
- Symptoms you're experiencing, such as jaw pain, headaches, or disturbed sleep
- Your complete medical and dental history to identify potential underlying causes
- Whether you need immediate intervention or if monitoring the condition is sufficient
Treatment Options and Solutions
Managing bruxism's impact on your dental health involves several effective treatment options, ranging from protective devices to therapeutic approaches. Your dentist may recommend custom-fitted mouth guards or splints, which create a protective barrier between your teeth during sleep bruxism and help reduce jaw muscle strain from clenching and grinding.
If stress triggers your teeth grinding, you'll benefit from stress management techniques like meditation, yoga, or cognitive-behavioral therapy. These methods can address the root causes of your bruxism while providing long-term relief. For severe cases, your healthcare provider might prescribe medications or recommend Botox injections to relax overactive jaw muscles.
Physical therapy exercises can strengthen and rebalance your jaw muscles, helping to prevent future episodes of grinding. You'll learn specific movements and techniques to maintain proper jaw alignment and muscle function. Additionally, if long-term teeth grinding has caused dental damage, you may need corrective dental procedures such as occlusal adjustments or restorative work. Your dentist will evaluate the extent of wear and determine the most appropriate treatment to restore your teeth's function and appearance.
Natural Remedies and Prevention

While medical treatments offer effective solutions for bruxism, natural remedies and lifestyle changes can provide vital relief without intervention. You can take control of your teeth grinding by incorporating stress-reduction techniques into your daily routine. Meditation, yoga, and deep breathing exercises work together to address the underlying anxiety that often triggers bruxism.
Your sleep habits play a pivotal role in managing teeth grinding. Maintaining proper sleep hygiene through a consistent sleep schedule and creating a relaxing bedtime routine can greatly reduce nighttime bruxism. You'll also want to be mindful of stimulants that can interfere with your sleep quality.
- Avoid caffeine, alcohol, and nicotine, especially in the hours before bedtime
- Engage in regular physical exercise to reduce muscle tension and stress
- Practice proper posture and ergonomics during work hours to minimize jaw and neck strain
- Establish a calming pre-bed routine that includes relaxation techniques
When to Seek Medical Help
Most symptoms of teeth grinding warrant professional attention, especially when they begin to affect your daily life. If you clench your teeth regularly or notice damage to your tooth enamel, it is indispensable to schedule a regular dental checkup. Your dentist or doctor can evaluate the severity of your bruxism and recommend appropriate treatments.
Don't hesitate to seek medical help if you're experiencing sleep-related disorders accompanied by teeth grinding. While activities like listening to music might temporarily help, professional intervention is often necessary when bruxism affects your sleep quality or leads to persistent jaw pain and headaches. Medical conditions like gastroesophageal reflux can sometimes contribute to teeth grinding, making it imperative to identify underlying causes.
If anxiety or stress causes bruxism, consider consulting both a dental professional and a mental health specialist. They can work together to address both physical and psychological factors contributing to your teeth grinding. For parents, it is particularly important to have children evaluated if they show signs of teeth grinding, as early intervention can prevent long-term dental problems. Remember, proper diagnosis and treatment are key to managing this condition effectively.




